print binary using shift and masking#
8 bit int#
lets play with small number first, imagine we want print 200 into binary, which is 0b11001000, this is how I do
step 0#
identify how many bits we need? say, char has 1 byte, int has 4 byte, long long has 8 byte. just multiply it with 8. you’ll get the bit.
1 * 8 = 8 bit
4 * 8 = 32 bit
8 * 8 = 64 bit
step 1#
mask, lets see this pattern
0b11001000
0b10000000
---------- &
0b10000000
see? 0b10000000, which is 0x80, what about 0x8? its 0x1000. find that? by shift left the bit, we turn 0x8 into 0x80
lets follow this pattern
0x8 << 0 = 0x8 (4 bit)
0x8 << 4 = 0x80 (8 bit) <— this is mask
0x8 << 8 = 0x800 (12 bit)
0x8 << 12 = 0x8000 (16 bit) <— this is mask
0x8 << 16 = 0x80000 (20 bit)
when I want mask 8 bit int? the mask is 0x80 because its perfectly fit 0b10000000, if I want mask 16 bit int? the mask is 0x8000, because its fit 0b1000000000000000 16 bit int, can filter the MSB
conlusion: the mask that we will use, is
0x8 << BIT_SIZE - 4
SAY, BIT_SIZE is 8 (eight bit int), 8 - 4 is 4, 0x8 << 4 = 0x80
same thing with
BIT_SIZE is 16, then 16 - 4 = 12, 0x8 << 12 = 0x8000
okay, the mask has been clearly explained
step 3, shifting#
say, I have 8 bit int. 0b11100011, when I mask it
n = 1#
0b11100011
0b10000000
---------- &
0b10000000
lets continue shift to left
n = 2#
0b11000110
0b10000000
---------- &
0b10000000
n = 3#
0b10001100
0b10000000
---------- &
0b10000000
n = 4#
0b00011000
0b10000000
---------- &
0b0000000
n = 5#
0b00110000
0b10000000
---------- &
0b00000000
n = 6#
0b01100000
0b10000000
---------- &
0b00000000
n = 7#
0b11000000
0b10000000
---------- &
0b10000000
n = 8#
0b10000000
0b10000000
---------- &
0b10000000
obtaining result#
lets see this pattern
0b10000000 0b10000000 0b10000000 0b0000000 0b00000000 0b00000000 0b10000000 0b10000000
if we use if else, to match whatever one byte is same as 0b10000000 or not, we will get result
1110 0011
YES, we successfully turn int 8 bit into binary presentation
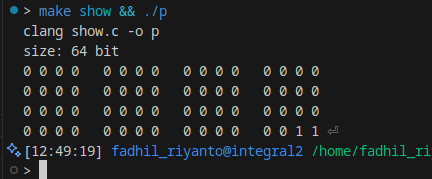
example#
#include <stddef.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
long long x = 3;
size_t BIT_SIZE = sizeof(x) * 8;
printf("size: %zu bit\n", BIT_SIZE);
long long big_mask = (0x8ULL << (BIT_SIZE - 4));
int counter = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < BIT_SIZE; i++) {
if (i % 4 == 0 && i != 0) {
printf(" ");
}
if (i % 16 == 0 && i != 0) {
printf("\n");
}
long int y = x & big_mask;
printf("%d ", y == big_mask ? 1 : 0);
x = x << 1;
}
}